Smartphone-Based Irrigation Information in Vineyards
Overview
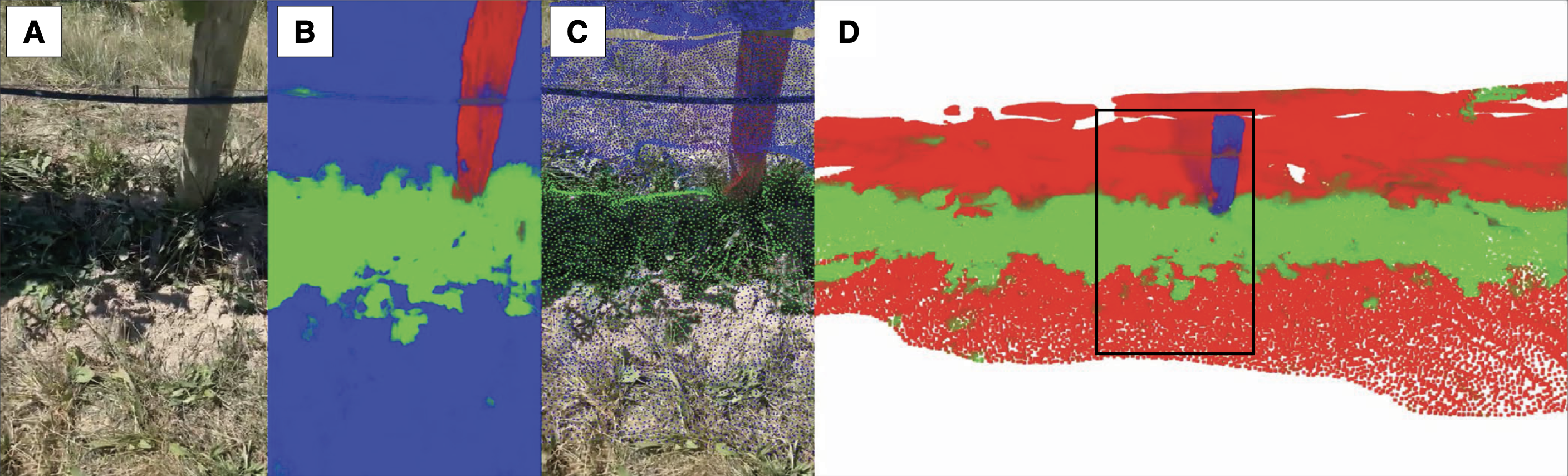
This project reimagines how farmers can measure vine water needs using a tool nearly everyone has — a smartphone. Traditionally, estimating how much water grapevines need requires expensive tools or tedious manual measurements. Instead, we developed a computer vision system that processes video of vine shadows captured from a smartphone to calculate the “crop coefficient,” a key metric used to guide irrigation decisions.
We built a pipeline that turns videos into 3D reconstructions of the ground beneath the vines and uses machine learning to identify shaded areas. The results were benchmarked against a commonly used solar panel-based method and achieved good agreement, with significant improvements in usability and speed.
Objectives
- Provide a low-cost, scalable method for measuring crop water demand.
- Replace manual or expensive measurement tools with computer vision.
- Demonstrate that a smartphone can reliably estimate shaded area beneath vines, a proxy for water use.
Description
The tool uses video taken under the vines and runs a machine learning pipeline that:
- Reconstructs a 3D model of the vineyard floor using structure-from-motion.
- Segments the shaded and sunlit areas using a neural network.
- Quantifies the shaded surface area to estimate the crop coefficient.
This process allows a single person with a phone to scan an entire row of vines in under a minute, replacing methods that traditionally take 10–15 minutes and require two people.
Impact
By making it easier and faster to measure crop coefficients, this project helps farmers better understand vineyard water usage. This can lead to more precise irrigation, saving water and improving grape quality. The method is accessible, fast, and requires no specialized hardware beyond a smartphone — making it especially valuable for small and medium-sized growers.
Future Work
- Integrate GPS data to map measurements across an entire vineyard.
- Extend the system to work in vineyards with different ground covers (e.g. bare soil or mulch).
- Make the software accessible through a user-friendly app or through integration with tools like the myEfficientVineyard platform.